«NASA» is an abbreviation for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, which is an American agency responsible for the United States’ space program.
Since its founding in 1957, during the era of former US President Dwight Eisenhower, NASA has worked on a wide range of space projects and research with a peaceful scientific dimension.
The race to space has begun overheating between Russia and the United States of America. After the Soviet Union announced the launch of Sputnik-1 on October 4, 1957, as the first human-made satellite, the United States considered this a threat , threatening its technical leadership, which prompted NASA to prepare programs to discover Space, the beginning was with the Mercury program.
G4 communications on the surface
of the Moon
NASA announced at the end of October of this year that it will allocate $ 14.1 million to finance a project in partnership with Nokia a Communications Corporation, with the aim of building a 4G mobile phone network to be located near the south pole of the moon!
This will not be the only goal of the astronauts of the Artemis mission, scheduled to land on the moon in 2024, but NASA is seeking through this to develop a system for generating and storing energy using materials from the moon itself.
This mission will be the first since the Apollo lunar mission in 1972, which an astronaut will land on the surface of the moon, but the difference this time is that the Artemis mission will witness the successful landing of the first woman on the moon, so the members of the team will be able to Connect to Earth whenever they want, thanks to this partnership that will bring together NASA and Nokia.
Of course, such amazing news about the recruitment by NASA of an outside agency is considered a very common thing since the sixties, this reach out collaboration is appreciated by the general public because it brings the awareness that has always been associated with scientific development and geniuses of scientists who have become superheroes.
In fact, they are as well, perhaps to a lesser degree compared to stories provided by cinema in terms of space, but they do through NASA providing a noble service to all mankind, as they facilitate human life and protect the earth, to discover another space in which we may live in the future.

Mercury Program
The Mercury program began in 1958,
it was aimed at placing a manned spacecraft in an orbital flight around earth in addition to investigating human capabilities to work in space environment, of course retrieving astronauts and spacecraft safely at the end of each mission, thus bringing NASA closer to reaching a provision : The possibility of man traveling to space with missions designed to see if a person can survive and live in space.
On April 9, 1959, Dr. Keith Glennan the agency’s chief executive back then announced the first crew of NASA, now known as Mercury 7 (Original Seven).
The crew included three marine pilots, three pilots from the Air Force and one from the Marine Corps: Leroy Cooper, Walter Shira, Alan Shepard, Virgil Grisom, John Glenn, Donald Slayten and Malcolm Carpenter.
Mercury became NASA’s first major project, its flights demonstrated that humans could live and work in space, it paved the way for Gemini and Apollo programmatic flights later, as well as many subsequent spaceflight.
The Apollo Program
The Soviet Union was the first country to send a person into space, as the Russian pioneer Yuri Gagarin won that honor in 1961 he was able to enter the Earth’s orbit and revolve around it, so the United States of America had to raise the ceiling of the challenge in the framework of the so-called Cold War between them and the Soviet Union, the US President John F. Kennedy made an open challenge to the world in the same year, saying that America would be able to land astronauts on the surface of the Moon at the end of the decade.
It was the most important goal of NASA’s Apollo space program, as it was able to carry out a total of 11 space flights, during which, it was able to achieve its goal of landing on the surface of the moon in intervals and in a gradual manner.
The first four flights involved testing the equipment used in the Apollo program and its efficacy before landing six of the other seven flights on the surface of the moon.
To carry out the mission to reach the moon as part of the Apollo program, NASA designed the Command Module, which is a capsule that can accommodate three astronauts.
Another spacecraft, the Lunar Module, was also used to land on the surface of the moon, meaning that astronauts would get out of their orbit around the moon to the surface and then return to orbit, but the lunar module was only accommodating two astronauts.
On July 20, 1969, during the Apollo 11 mission,
which included Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin, an Apollo spacecraft was launched on top of the Saturn V rocket (Saturn 5). Once the spacecraft reached the moon, the two units separated from each other.
Neil Armstrong walked first on the moon’s surface, then Aldrin ,while Collins remained in orbit around the moon.Neil famous phrase”That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.»
President John F. Kennedy fulfilled his promise regarding the landing of humans on the surface of the moon, NASA also succeeded in this challenge with the Apollo program, this was the first time that humans left Earth’s orbit to visit another world, which opened the appetite of the agency and others to explore more distant worlds in the future.
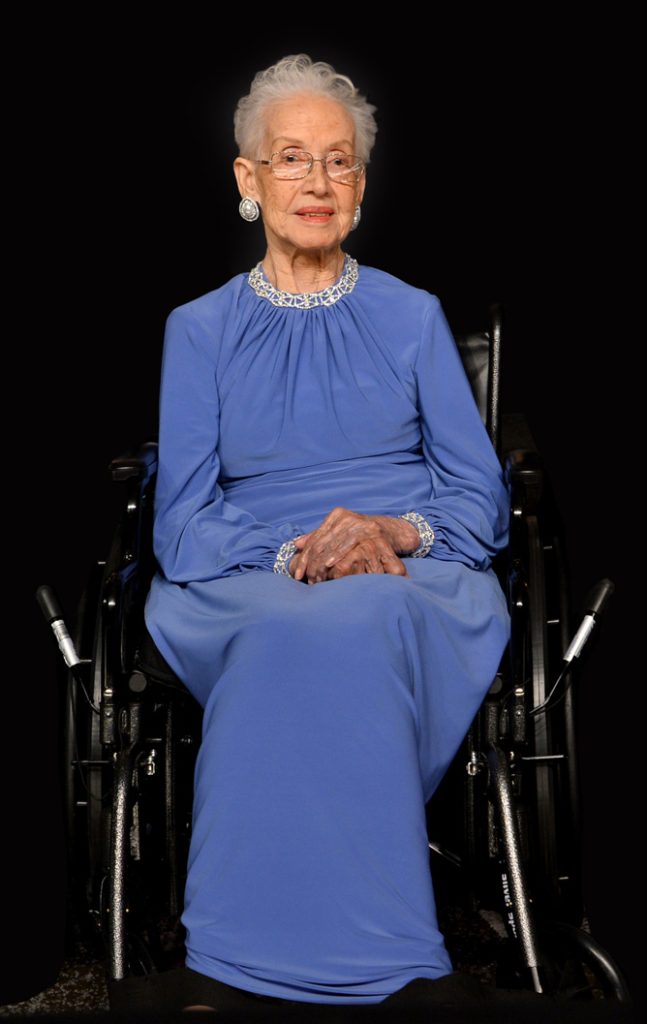

Katherine Johnson
Star facilitated the mission to reach the moon!
The first space flight of the Apollo program took place in 1968, it was the first human landing
on the moon’s surface one year later, the last landing was in 1972. A total of 12 astronauts walked on the surface of the moon, conducted scientific research, studied its surface and collected rocks to bring back to Earth, here we are today, preparing for a project to establish a fourth generation telecommunications company somewhere on the moon!
But all of this did not come easily, thanks to the efforts of many who we may have heard about or those whose identities we still do not know today, among these is the mathematician Katherine Johnson!
Katherine Johnson passed away in February 2020 at the age of 101. The deceased was nicknamed by the agency “the NASA computer” a nickname she earned.
Katherine was behind writing all the accounts of the Apollo‘s 11 path to the moon, a journey during which Neil Armstrong was able to walk on its surface to make history, with those who participated and prepared for it, the most important of them is Katherine Johnson, she was one of the few American women who worked as a «computer.»
to inspect and verify the engineers’ accounts at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), the predecessor agency to NASA.
She was honored by US President Barack Obama in 2015 when she received the Presidential Medal of Freedom, in gratitude for her contribution to the first moon landing.
This scientist who specialized in the calculations of «orbital mechanics», which is a very complex process at the time, needed amazing accuracy, before the availability of the computers that we know today. For example, Katherine was behind the determination of the flight path of Alan Shepard in 1961, the first American in space.
Even after the availability of the most advanced computers, John Glenn, who was preparing for his first trip around the planet in 1962, used them to check mathematical calculations on their own because he did not trust electronic computers.
Otherwise, Katherine Johnson took part in several other flights before retiring in 1986.
Katherine Johnson did not leave this world until she saw her life story, which was turned into a 2016 movie entitled «Hidden Figures».
Colombia – An achievement that falls from the sky
While passing through the airspace of the town of Palestine in the city of Dallas, the capital of the state of Texas, on February 1, 2003, exactly at 00.14 GMT, NASA lost contact with the American shuttle Columbia, which was on its way back to Earth after a space mission.
Colombia disappeared from the radar screens, after the American television networks broadcasted its fragmentation as it entered the Earth’s atmosphere at a speed of six times the speed of sound at a height of 60 km with seven astronauts on board.
A difficult birth!
At the beginning of the construction of the space shuttle in 1975 by the main assembly facility on the outskirts of Los Angeles, it was expected to discover the outside world, therefore it was named Colombia after the Columbia Rediviva, the first American ship to sail around the world under the command of explorer Captain Robert Gray in 1787 and 1793.
NASA was unable to launch Colombia as planned
at the end of 1979, but was forced to postpone that date due to problems with both the RS-25 engine and the thermal protection system (TBS).
These were not the last problems facing the oldest American space shuttle, as on March 19, 1981, during preparations for the ground test before its launch, workers choked while working in the aft compartment of a nitrogen-purge engine, leading to the death of two people.

Successful but last mission!
Colombia then undertook 28 space missions, the last of which lasted 16 days, aimed at conducting an experiment in satellite communication via the Internet, in addition to a German research program on the effect of zero gravity on animals before it ended in a disaster on it’s way home.
Commander Rick Hasband, Pilot Willie McCall, mission specialists Dave Brown, Laurel Clarke, Kalpana Chawla, Payload Commander Mike Anderson, and astronaut specialist Ilan Ramon are the pioneers who were on board the spacecraft when it exploded.
A video tape – then retrieved – recorded by the pioneers during the start of the return showed that the crew members were performing routine re-entry procedures and joking with each other, but the recording process that would have continued on the regular flights until the landing was stopped four minutes before the start of the shuttle disintegration.
Experts attributed the causes of the crash to a defect in the thermal insulation that protects the shuttle when returning to Earth from high temperatures.
One side of this insulation was destroyed in the shuttle’s black bottom part by hitting spongy pieces of insulation that covered its main fuel tank with one of its wings upon takeoff. Then, during the return trip to Earth, hot gases leaked through the damaged heat insulator to find their way to the shuttle and led to Last blast.
Images broadcast by the American television network «CNN» at the time revealed white lines behind Columbia as it passed through the atmosphere of Dallas, enhancing the possibility that it exploded while entering the Earth’s atmosphere.
Sky Lab
It is the first and only space station launched by the United States of America alone without the participation of any other country, it is considered the second space station to orbit in Earth after the Russian Mir station.
The Sky Laboratory was launched on May 14, 1973 to orbit the Earth at an altitude of 435 km from the surface of Earth.
Upon its launch, the station faced a number of problems, the most important of which was the separation and breakage of most of the solar cells responsible for generating energy, which led to an acute shortage of electricity.
The matter was remedied and the laboratory was repaired in its first manned flight on May 25, 1973, followed by two manned flights on July 28, 1973 and November 16, 1973, to be evacuated by astronauts on February 8, 1974.
During this period, the laboratory rotated 2,476 times around the Earth in 171 days and 13 hours, and a total of 2,000 hours of scientific and medical tests were held in ii, aimed at finding out the effect of zero gravity on astronauts, and on July 11, 1979, the SkyLab lost its height and entered the Earth’s mantle then fell.
The International Space Station ISS
The idea of the International Space Station came through a Russian proposal in March 1993, when the Director General of the Russian Space Agency «Mir» Yuri Koptev proposed to the Director of the American «NASA» agency, Daniel Goldin, the establishment of an international space station.
The implementation of the project began on September 2, 1993, after it was agreed to officially name the «International Space Station» or ISS, which is short for International Space Station a new era.
A group of countries joined Russia and the United States of America to build the station in an international cooperation under the leadership of the afore mentioned, along with Canada, Japan, and other European countries, namely Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Netherlands, Norway, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland. The United Kingdom, in addition to Brazil, the cost of the station was estimated at more than 150 billion dollars, NASA contributed about 72.4 billion dollars, Russia about 12 billion dollars, while Europe contributed about 5 billion dollars, Japan 5 billion dollars, and Canada about 2 billion dollars.
The International Space Station was launched for the first time on November 20, 1998 and was mainly aimed at preparing people to spend long time in space, conducting experiments outside the area of Earth’s gravity, and working to improve the quality of life on Earth by increasing scientific knowledge through research in addition to its various Space exploration.
Astronomical numbers!
The ISS weighs half a million kg and orbits at an altitude between 370 and 460 km above the surface of the Earth. Goes to 28 thousand km per hour, it can get to the moon and return in less than 24 hours, the International Space Station completes one revolution around the Earth every 90 minutes, it rotates around 16 times a day, which exposes the astronauts to witnessing 16 sunrise and sunset in the same day.
So, to avoid confusion, they set the average time (Greenwich) as the one on board, and when the sun sets in London, the station windows are closed
automatically to give the patrons a feeling of night sleep.
The international station is controlled from the ground by two stations, the first in Houston in the United States of America and the second in Moscow, the capital of Russia. As for its operating energy, it does not depend on fuel in its known sense, but rather uses huge solar cells on both sides to generate energy, while the length of the station extends to about (109 meters). It’s width to (72.8 meters) is the size of a large football field, and it gives the astronauts of the International Space Station a lot of comfortable rooms for eating and sleeping periods.

The age of the International Space Station
The ISS financing program was established in 1998 with the hope that it would operate for about 15 years, then it was extended with additional financial support from the countries supporting it, led by the United States through NASA, it is assumed that the support will continue until about 2024 at the latest, because NASA will shifts its focus to supporting the manned missions of the moon and Mars over the coming decades.